cytoplasm
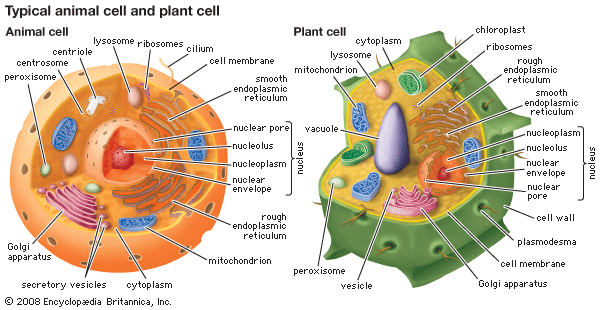
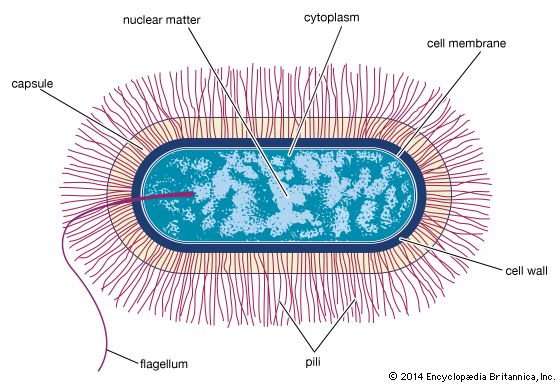
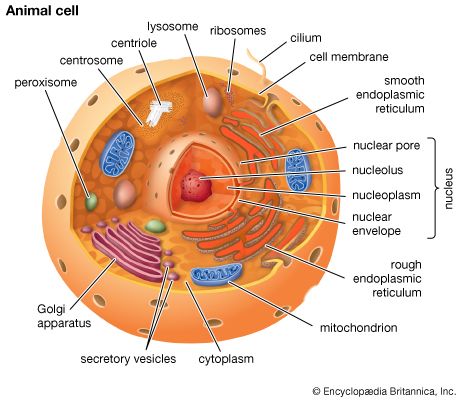
cytoplasm, the semifluid substance of a cell that is external to the nuclear membrane and internal to the cellular membrane, sometimes described as the nonnuclear content of protoplasm. In eukaryotes (i.e., cells having a nucleus), the cytoplasm contains all of the organelles.
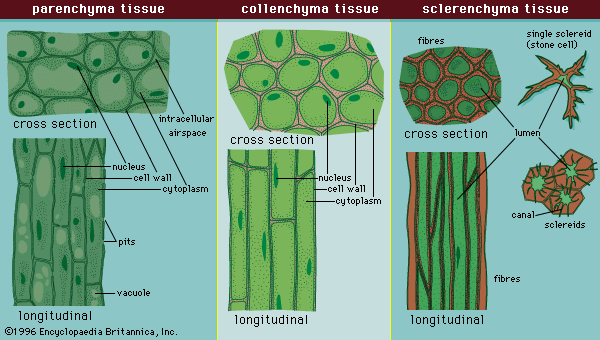
Among such organelles are the mitochondria, which are the sites of energy production through ATP (adenosine triphosphate) synthesis; the endoplasmic reticulum, the site of lipid and protein synthesis; the Golgi apparatus, the site where proteins are modified, packaged, and sorted in preparation for transport to their cellular destinations; lysosomes and peroxisomes, sacs of digestive enzymes that carry out the intracellular digestion of macromolecules such as lipids and proteins; the cytoskeleton, a network of protein fibres that give shape and support to the cell; and cytosol, the fluid mass that surrounds the various organelles.
-
What are organelles and how do they function in a cell?
-
How do mitochondria produce energy for the cell?
-
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-
How does the endoplasmic reticulum help build proteins?
-
Why is the cytoskeleton important for cell structure and movement?